
一: 搭建基于 jest 的 vue 单元测试环境
二: 使用 vue-test-util 提高测试编码效率
三: 复杂场景下的测试(模块,异步,rxjs)
搭建基于 jest 的 vue 单元测试环境
因为 jest 包含了 karma + mocha + chai + sinon 的所有常用功能,零配置开箱即用,所以这个教程只讲解 jest。
安装依赖
npm install jest vue-jest babel-jest @vue/test-utils -D
配置文件
// ./test/unit/jest.conf.js
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
rootDir: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../'), // 类似 webpack.context
moduleFileExtensions: [ // 类似 webpack.resolve.extensions
'js',
'json',
'vue',
],
moduleNameMapper: {
'^@/(.*)$': '<rootDir>/src/$1', // 类似 webpack.resolve.alias
},
transform: { // 类似 webpack.module.rules
'^.+\\.js$': '<rootDir>/node_modules/babel-jest',
'.*\\.(vue)$': '<rootDir>/node_modules/vue-jest',
},
setupFiles: ['<rootDir>/test/unit/setup'], // 类似 webpack.entry
coverageDirectory: '<rootDir>/test/unit/coverage', // 类似 webpack.output
collectCoverageFrom: [ // 类似 webpack 的 rule.include
'src/**/*.{js,vue}',
'!src/main.js',
'!src/router/index.js',
'!**/node_modules/**',
],
};
启动文件
// ./test/unit/setup.js
import Vue from 'vue';
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
4.加入启动 jest 的 npm script
"scripts": {
"unit": "jest --config test/unit/jest.conf.js --coverage",
},
编写测试
有一个组件
// ./src/components/hello-world/hello-world.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data() {
return {
msg: 'Hello Jest',
};
},
};
</script>
对该组件进行测试
// ./src/components/hello-world/hello-world.spec.js
import { shallowMount } from '@vue/test-utils';
import HelloWorld from './hello-world';
describe('<hello-world/>', () => {
it('should render correct contents', () => {
const wrapper = shallowMount(HelloWorld);
expect(wrapper.find('.hello h1').text())
.toEqual('Welcome to Your Vue.js App');
});
});
启动测试
npm run unit
jest 会自动扫描项目目录下所有文件名以 .spec.js/.test.js 结尾的测试文件,并执行测试用例。
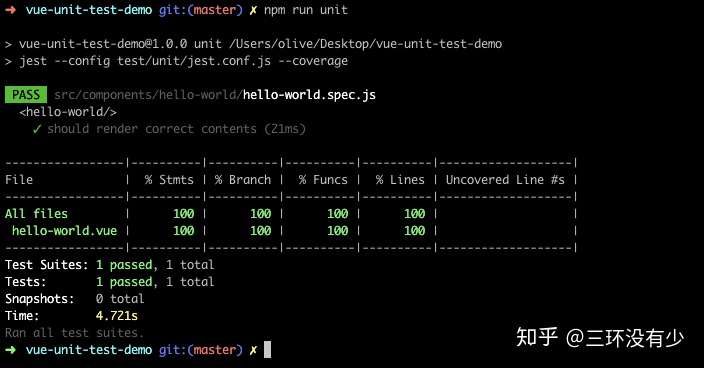
最后优化一下测试编码体验
到上一步我们已经可以开始编写测试代码了,但每次对代码的改动都需要手动执行 jest 启动命令,没有类似 hot-reload 的功能很难受。
可能你有一百种方式可以解决这个需求,但是我现在想告诉你一个最简单且体验最好的一种方式 -> 在 vscode 编辑器安装一个名为 jest 的插件
但是安装后它可能还不能很好的工作,因为 vscode-jest 暂时并不知道我们的 jest 配置文件在哪里。
你可以选用下面任意一种方式解决这个问题:
\1. 修改 vscode 配置文件,将 jest.pathToConfig 指向我们刚才编写的配置文件
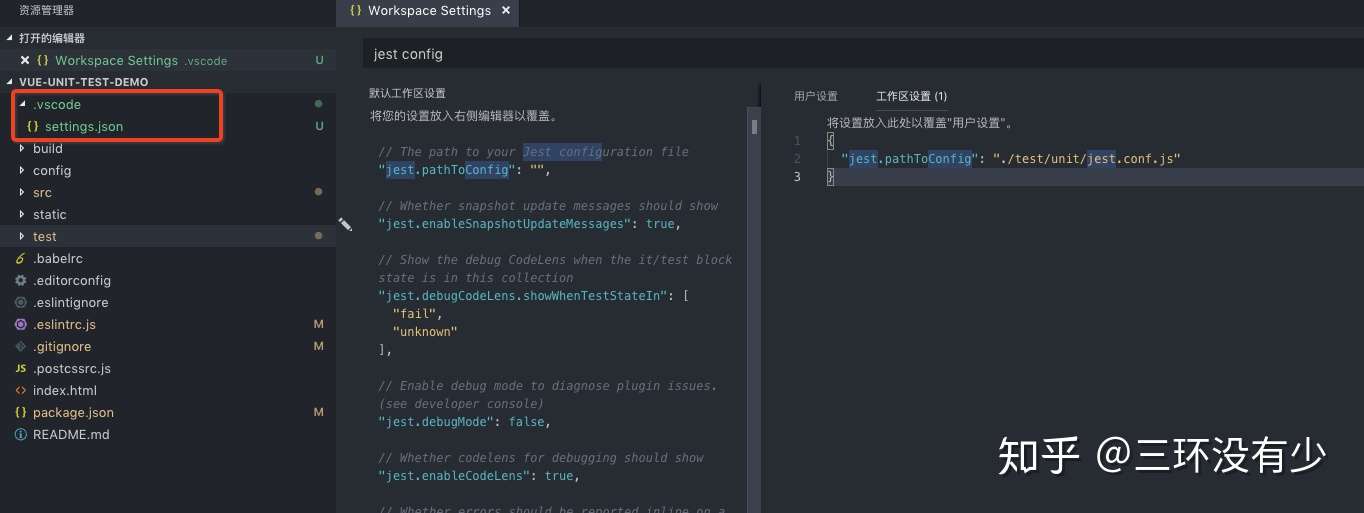
\2. 将 jest 配置写在 package.json 中的 jest 字段
\3. 将 jest 配置文件提到项目根目录,并且更名为 jest.config.js 或者 jest.json
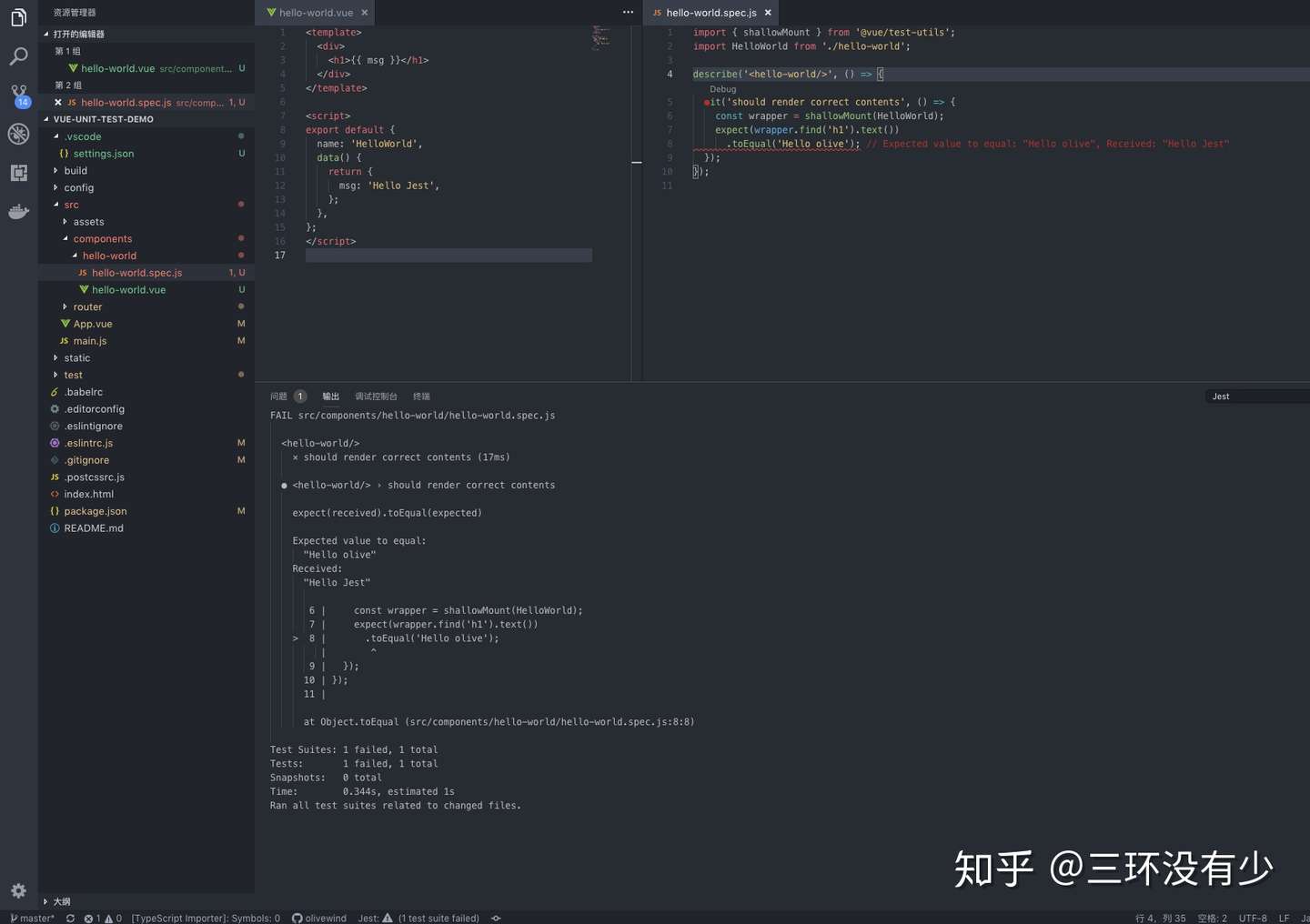
现在 vs-code-jest 会根据 git 修改记录自动执行应该执行的测试文件,并在控制台实时给出测试结果。至此第一部分大功告成。
使用 vue-test-util 提高效率
因为 vue-test-util 的官方文档写的实在是太好了,不再赘述其 API,重点说明一点,为什么推荐使用 vue-test-util 来编写 Vue 组件单元测试,因为它不仅提供了很多实用的 API ,还同步了 DOM 的更新,也就是说我们的测试代码里不会再充斥着 vm.$nextTick() 等代码,举个例子
有一个组件
// ./src/components/hello-world/hello-world.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<button @click="onClick">click me</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data() {
return {
msg: 'Hello Jest',
};
},
methods: {
onClick() {
this.msg = 'new message';
},
},
};
</script>
对该组件进行测试
// ./src/components/hello-world/hello-world.spec.js
import { shallowMount } from '@vue/test-utils';
import HelloWorld from './hello-world';
describe('<hello-world/>', () => {
const wrapper = shallowMount(HelloWorld);
it("update 'msg' correctly", () => {
// 点击 button
wrapper.find('button').trigger('click');
// 可以立即获取 msg 最新的值,不再需要 wrapper.vm.$nextTick();
expect(wrapper.find('h1').text())
.toEqual('new message');
});
});
如果需要做一些全局的 vue-test-util 的配置,可以在 setup.js 里指定,比如在每个组件实例化时候注入一个 GLOBAL 对象。
// ./test/unit/setup.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import { config } from '@vue/test-utils';
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
// provide 的模拟
config.provide.GLOBAL = {
logined: false,
};
有一个组件注入了 GLOBAL 对象
// ./src/components/hello-world/hello-world.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1 v-show="GLOBAL.logined">{{ msg }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
inject: ['GLOBAL'],
data() {
return {
msg: 'Hello Jest',
};
},
};
</script>
对该组件进行测试
// ./src/components/hello-world/hello-world.spec.js
import { shallowMount } from '@vue/test-utils';
import HelloWorld from './hello-world';
describe('<hello-world/>', () => {
const wrapper = shallowMount(HelloWorld);
it('should render correct contents', () => {
expect(wrapper.find('h1').isVisible()).toBe(false);
});
});
复杂场景下的测试
组件发起了API 请求,我只想知道它发没发,不想让它真实发出去
有一个组件在会在 created 时候发起一个 http 请求
// ./src/components/user-info/user-info.vue
<template>
<div class="user-info">
<div class="name">{{user.name}}</div>
<div class="desc">{{user.desc}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import UserApi from '../../apis/user';
export default {
name: 'UserInfo',
data() {
return {
user: {},
};
},
created() {
UserApi.getUserInfo()
.then((user) => {
this.user = user;
});
},
};
</script>
API 接口如下
// ./src/apis/user.js
function getUserInfo() {
return $http.get('/user');
}
export default {
getUserInfo,
};
对该组件进行测试
// ./src/components/user-info/user-info.spec.js
import { shallowMount } from '@vue/test-utils';
import UserInfo from './user-info';
import UserApi from '../../apis/user';
// mock 掉 user 模块
jest.mock('../../apis/user');
// 指定 getUserInfo 方法返回假数据
UserApi.getUserInfo.mockResolvedValue({
name: 'olive',
desc: 'software engineer',
});
describe('<user-info/>', () => {
const wrapper = shallowMount(UserInfo);
test('getUserInfo 有且只 call 了一次', () => {
expect(UserApi.getUserInfo.mock.calls.length).toBe(1);
});
it('用户信息渲染正确', () => {
expect(wrapper.find('.name').text()).toEqual('olive');
expect(wrapper.find('.desc').text()).toEqual('software engineer');
});
});
简单的 A 组件依赖了一个复杂的 B 组件,但是我只想测试 A 的逻辑,不想拉起 B 的逻辑
这种场景其实很常见,比如某些复杂组件 import 了某些会自执行的代码,这个时候为了保证单元测试的纯粹,我们应该忽略掉所依赖的子组件的逻辑。
// ./src/components/simple/simple.vue
<template>
<div>
<div class="header">{{msg}}</div>
<div>
<complex></complex>
// 即使 vue-test-util 可以通过存根的方式将这个组件渲染为 complex-stub
// 但其内部的其他代码可能依然被执行
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Complex from './children/complex';
export default {
name: 'Simple',
data() {
return {
msg: 'simple',
};
},
components: {
Complex,
},
};
</script>
对该组件进行测试
// ./src/components/simple/simple.spec.js
import { shallowMount } from '@vue/test-utils';
import Simple from './simple';
// 拦截掉 .vue 文件的内容
jest.mock('./children/complex.vue', () => ({
render(h) {
h();
},
}));
describe('<simple/>', () => {
const wrapper = shallowMount(Simple, {
stubs: ['user-info'],
});
it('文本渲染正确', () => {
expect(wrapper.find('.header').text()).toEqual('simple');
});
});
测试 Rx.JS
假设有一个 subject,订阅的时候会发射 ‘hello-rx’
// ./src/components/rx-demo/msg.stream.js
import { BehaviorSubject } from 'rxjs';
const msg$$ = new BehaviorSubject('hello-rx');
export default msg$$;
有一个组件订阅该 subject
// ./src/components/rx-demo/rx-demo.vue
<template>
<div class="rx-demo">{{msg}}</div>
</template>
<script>
import msg$$ from './msg.stream';
export default {
name: 'RxDemo',
data() {
return {
msg: '',
};
},
created() {
msg$$.subscribe((res) => {
this.msg = res;
});
},
};
</script>
对该组件进行测试
// ./test/utils/index.js
import { BehaviorSubject } from 'rxjs';
function mockSubject(data) {
return new BehaviorSubject(data);
}
export {
mockSubject,
};
// ./src/components/rx-demo/rx-demo.spec.js
import { shallowMount } from '@vue/test-utils';
import RxDemo from './rx-demo';
jest.mock('./msg.stream.js', () => {
//这一部分会被 babel-jest 提升到代码顶部,所以需要这么动态去 require 才可以保证代码顺序是正确的
const { mockSubject } = require('../../../test/unit/util');
return mockSubject('mock-data');
});
describe('<rx-demo/>', () => {
it('Rx 订阅成功,文本渲染正确', () => {
const wrapper = shallowMount(RxDemo);
expect(wrapper.find('.rx-demo').text()).toEqual('mock-data');
});
});
总得来说,把测试目标组件范围外的不好测试的模块全部 mock 掉,然后再根据你们对单元测试要求的细粒度进行断言。
其他简单场景不再做赘述,遇到问题请随时联系我,谢谢。